Maps of Greece and the Greek islands
The area of Greece, as we see on the following map, located at the most southerly part of the Balkan Peninsula and in the southeast of the Mediterranean Sea. To the north, borders Albania, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria. To the east, it borders the European part of Turkey.
The Ionian Sea lies to the west of Greece, while the Aegean Sea is to the east. To the south is the Libyan Sea. For more information about the geography of Greece, including details about its lakes, rivers, and mountains, as well as the geomorphology of the country, you can refer to the physical map of Greece.
With a coastline of 13,676 km, the country is boasting the longest coastline in the Mediterranean. Most of the Greek islands and islets are situated in the Aegean Sea, while a small number of islands are in the Ionian Sea.
In general, Greece is not densely inhabited. With a total surface area of 132,000 sq. km, Greece has a population of about 11,000,000 inhabitants. This is partly because much of the Greek mainland is mountainous, with a few plateaus in Thessaly, Macedonia, and Thrace, and a large part of the country consists of islands.
Therefore, most of Greece’s population is concentrated in the big urban centres, with Athens and its greater area, including Piraeus, housing one-third of the Greek population. This is followed by Thessaloniki, Patras, Heraklion, and Larissa.
Map of Greece

- Regions of Greece
- Greek Islands Map
- Climate map
- Satellite Map
- Prefectures of Greece
- Location of Greece
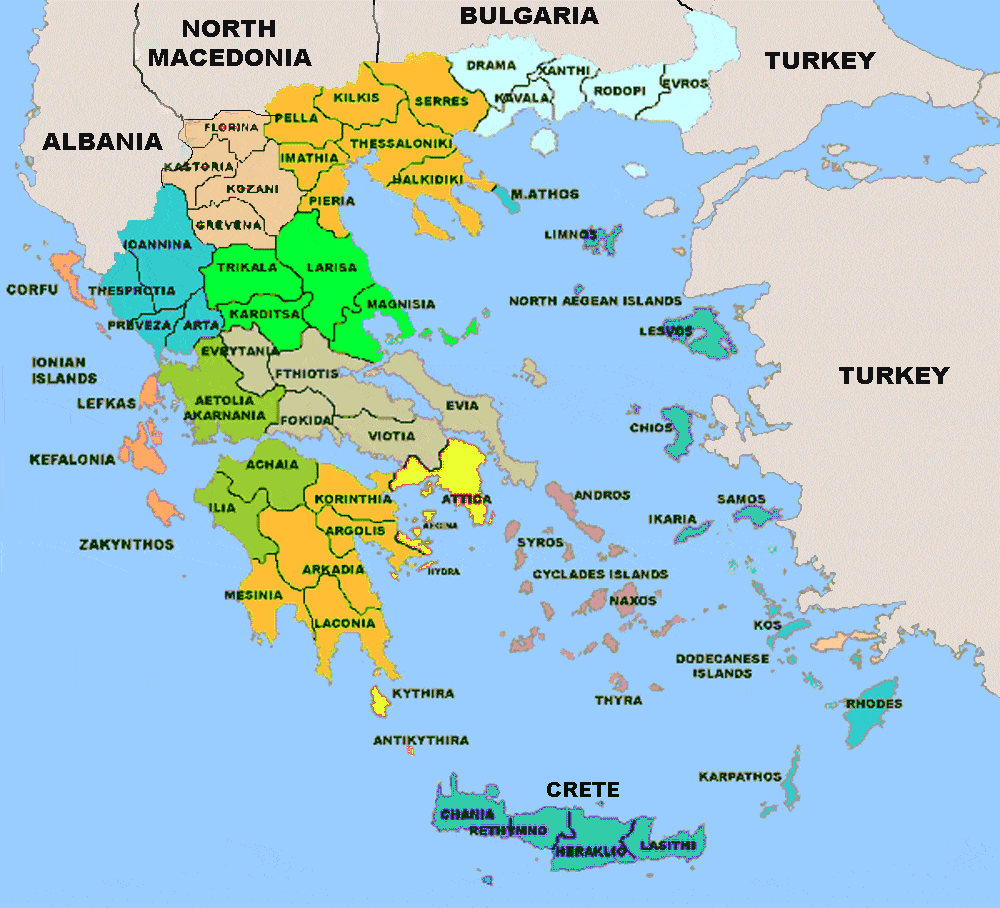
Greek regions map
Greece is divided into 13 regions or peripheries. Macedonia (6) with Thrace (7) in the north and north west, Epirus (5) in the north west , Thesally (4 ) and Sterea Ellas with Evia (3) in the centre ,the Peloponesse (2) in the south, Attica (1). The Ionian islands in the west (13) , the East Aegean islands (9) and the North Aegean islands (8) , Cyclades (11) ,Dodecanese (10) , At the southern tip lies the largest island of Greece Crete (13)

Greek Regions Map
Climate Map
This map aims to examine the varied climate characteristics of Greece and understand their impact on the Greek natural environment and human life. Being a Mediterranean state, Greece is predominantly characterized by a Mediterranean climate. This climate features hot and dry summers, along with moderate to cold, rainy winters.
The coastal regions and islands of Greece enjoy a particularly mild climate, boasting many sunny days each year. This significantly contributes to the development of tourism in these areas. In contrast, the inland and mountainous regions experience more varied climatic conditions.
Here, the continental climate prevails, marked by stronger seasonal changes. Winters are colder with snowfall being common, especially in the mountainous areas. Summers, while remaining hot, are often less dry than in the coastal areas.
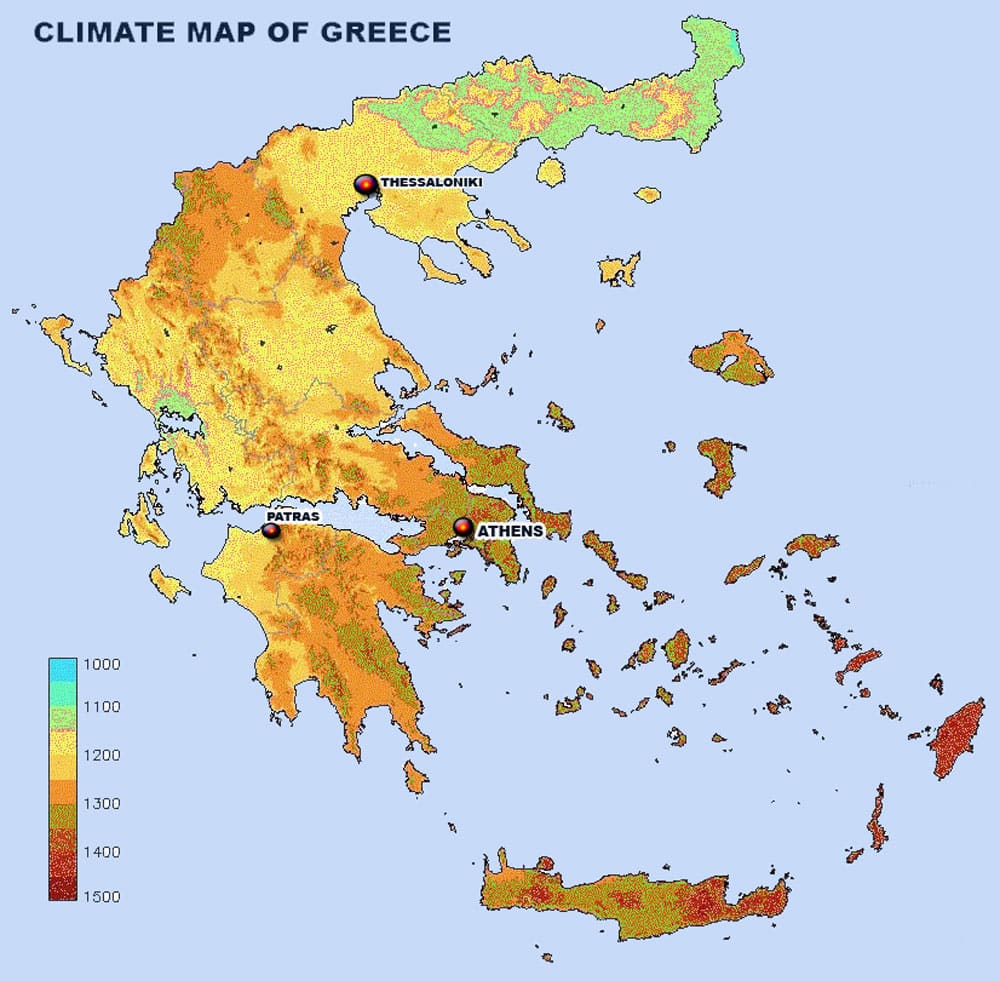
GREECE CLIMATE MAP
Satellite Map of Greece
The satellite map of Greece presents an image of the country as captured by satellites in space. This image encompasses various aspects, including the geographical configuration, the distribution of towns and villages, transport networks, physical features, the Greek islands and other significant elements.
Greek Prefectures
Greek islands
The Greek island groups of the Cyclades and the Dodecanese extend from Central Greece to the coasts of Asia Minor. The island arc formed by Kithira, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes connects the Peloponnese with the coasts of Asia Minor.

Sporades islands

This cluster consists of four main inhabited islands, Alonissos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros. , alongside numerous smaller, uninhabited islets.
The cartographic representation of the Sporades reveals both the physical layout of these islands and provides insights into their historical and ecological significance.

The Cyclades emerge from the blue of the Aegean with wonderful beaches and typical white and blue houses. The fascinating archipelago of the Cyclades consists of a group of islands of various sizes scattered in the blue waters of the Aegean Sea southeast of Attica.
These islands are primarily composed of rocky terrain and are known for their hilly landscapes, with the highest peak found on Naxos, Mount Zeus, reaching an elevation of approximately 1,004 meters.
Some of them are internationally known, such as Santorini, Mykonos, Paros, Syros, Ios and Naxos, while others remain less known and less touristy.
Some of them are internationally known, such as Santorini, Mykonos, Paros, Syros, Ios and Naxos, while others remain less known and less touristy, but also beautiful such as Milos, Folegandros, Amorgos and others. The name of this group of islands comes from the Greek word Cycle and identifies the location of the islands around Delos, the sacred island of Apollo.

The climate of the East Aegean Islands is predominantly Mediterranean, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. This climate supports a wide variety of vegetation, from olive groves and vineyards to dense forests in certain areas. The geographical position of these islands also means they are subject to the meltemi, strong north winds that are particularly prevalent in the summer.
East Aegean islands are: Thasos, Samos, Samotraki, Ikaria, Chios, Lesbos, Limnos, Agios Efstratios, Psara, Fourni, Oinouses.Demarcating the border between Greece and Turkey.

The group consists of twelve major islands, hence the name “Dodecanese,” derived from the Greek word “dodeka,” meaning twelve, as well as numerous smaller islets.
The islands are dispersed across a maritime landscape that has played a crucial role in the cultural and economic exchanges of the eastern Mediterranean.
Among them from North to the South are the islands of Agathonisi, Patmos, Lipsi, Leros, Kalymnos, Kos, Nisyros, Symi, Rhodes, Kasos , Karpathos and Kastellorizo.

The strategic locations of the islands in relation to Athens and the Peloponnesian coast highlight their roles in ancient and modern maritime activities. The Saronic Islands continue to attract scholars, tourists, and historians, drawn by their unique combination of historical landmarks, natural beauty, and vibrant local cultures. The main islands in the Saronic group include Aegina, Poros, Hydra, Spetses, and Salamis.
These islands are known for their varied landscapes, which include rocky terrain, small fertile plains, and a mix of sandy and pebbly beaches. The topography of these islands is generally hilly, with the highest point found on Aegina, known as Mount Oros, which reaches about 532 meters in elevation.
Location of Greece in the South East Europe

Other Maps
